Instrumenting calls to a PostgreSQL database
Note
X-Ray SDK/Daemon Maintenance Notice – On February 25th, 2026, the Amazon X-Ray SDKs/Daemon will enter maintenance mode, where Amazon will limit X-Ray SDK and Daemon releases to address security issues only. For more information on the support timeline, see X-Ray SDK and Daemon Support timeline. We recommend to migrate to OpenTelemetry. For more information on migrating to OpenTelemetry, see Migrating from X-Ray instrumentation to OpenTelemetry instrumentation .
The application-pgsql.properties file adds the X-Ray PostgreSQL
tracing interceptor to the data source created in RdsWebConfig.java
Example application-pgsql.properties
spring.datasource.continue-on-error=true
spring.jpa.show-sql=false
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
spring.datasource.jdbc-interceptors=com.amazonaws.xray.sql.postgres.TracingInterceptor
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQL94DialectNote
See Configuring Databases with Elastic Beanstalk in the Amazon Elastic Beanstalk Developer Guide for details on how to add a PostgreSQL database to the application environment.
The X-Ray demo page in the xray branch includes a demo that uses the
instrumented data source to generate traces that show information about the SQL queries that
it generates. Navigate to the /#/xray path in the running application or choose
Powered by Amazon X-Ray in the navigation bar to see the demo
page.
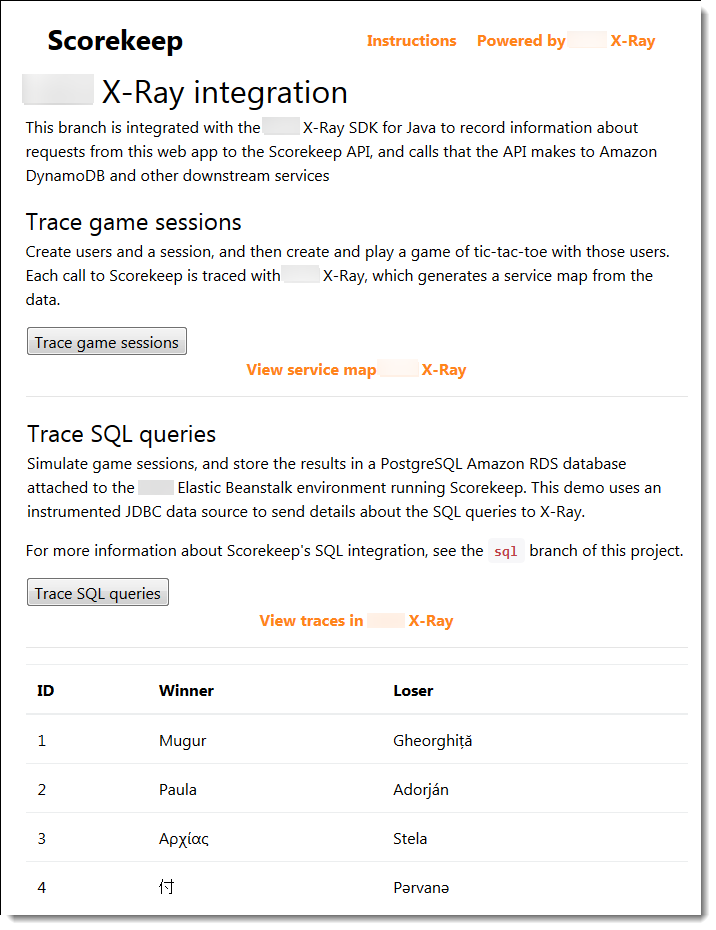
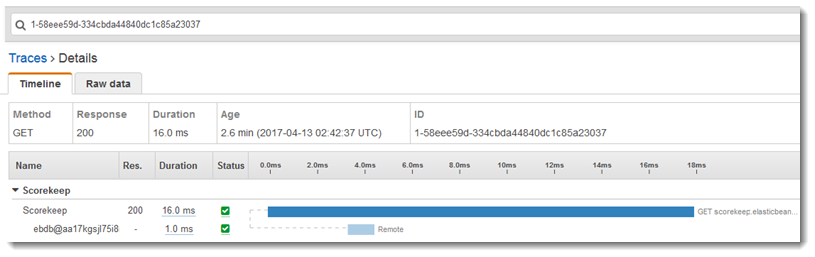
Choose Trace SQL queries to simulate game sessions and store the
results in the attached database. Then, choose View traces in Amazon X-Ray
to see a filtered list of traces that hit the API's /api/history route.
Choose one of the traces from the list to see the timeline, including the SQL query.