Viewing cluster status
Using the Amazon RDS console, you can quickly access the status of your DB cluster.
Topics
Viewing an Amazon Aurora DB cluster
You have several options for viewing information about your Amazon Aurora DB clusters and the DB instances in your DB clusters.
-
You can view DB clusters and DB instances in the Amazon RDS console by choosing Databases from the navigation pane.
-
You can get DB cluster and DB instance information using the Amazon Command Line Interface (Amazon CLI).
-
You can get DB cluster and DB instance information using the Amazon RDS API.
In the Amazon RDS console, you can see details about a DB cluster by choosing Databases from the console's navigation pane. You can also see details about DB instances that are members of an Amazon Aurora DB cluster.
To view or modify DB clusters in the Amazon RDS console
Sign in to the Amazon Web Services Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
-
Choose the name of the Aurora DB cluster that you want to view from the list.
For example, the following image shows the details page for the DB cluster named
aurora-test. The DB cluster has four DB instances shown in the DB identifier list. The writer DB instance,dbinstance4, is the primary DB instance for the DB cluster.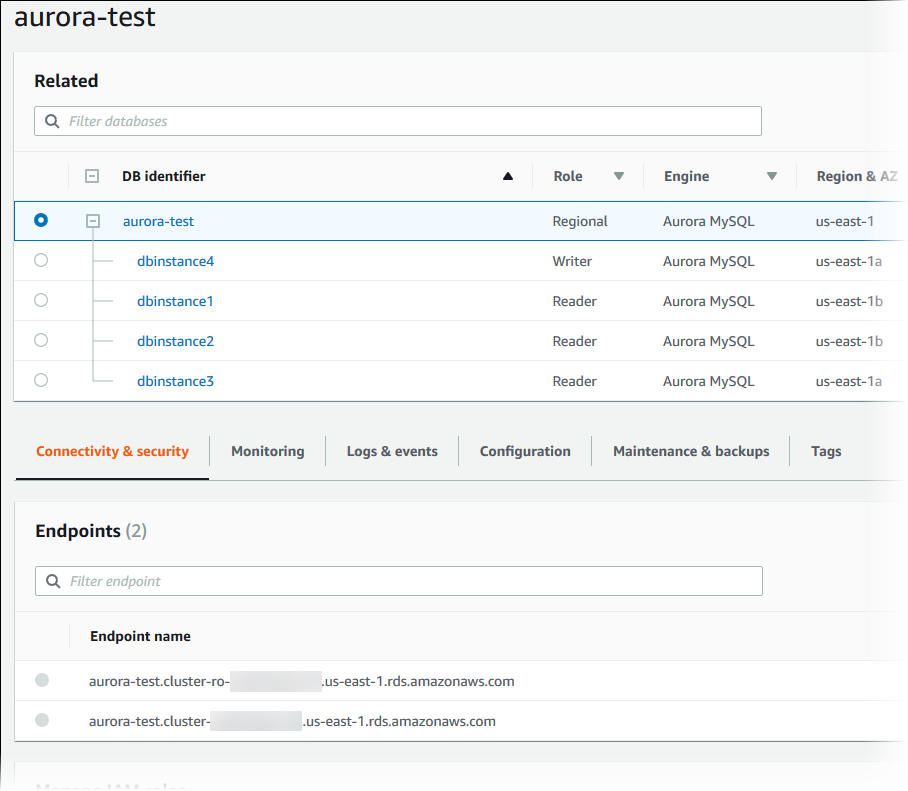
-
To modify a DB cluster, select the DB cluster from the list and choose Modify.
To view or modify DB instances of a DB cluster in the Amazon RDS console
Sign in to the Amazon Web Services Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To view a DB instance, choose one from the list that is a member of the Aurora DB cluster.
For example, if you choose the
dbinstance4DB instance identifier, the console shows the details page for thedbinstance4DB instance, as shown in the following image.
-
To modify a DB instance, choose the DB instance from the list and choose Modify. For more information about modifying a DB cluster, see Modifying an Amazon Aurora DB cluster.
-
To view DB cluster information by using the Amazon CLI, use the describe-db-clusters command. For example, the
following Amazon CLI command lists the DB cluster information for all of the DB clusters in the
modify us-east-1 region for the configured Amazon account.
aws rds describe-db-clusters --regionus-east-1
The command returns the following output if your Amazon CLI is configured for JSON output.
{ "DBClusters": [ { "Status": "available", "Engine": "aurora-mysql", "Endpoint": "sample-cluster1.cluster-123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com" "AllocatedStorage": 1, "DBClusterIdentifier": "sample-cluster1", "MasterUsername": "mymasteruser", "EarliestRestorableTime": "2023-03-30T03:35:42.563Z", "DBClusterMembers": [ { "IsClusterWriter": false, "DBClusterParameterGroupStatus": "in-sync", "DBInstanceIdentifier": "sample-replica" }, { "IsClusterWriter": true, "DBClusterParameterGroupStatus": "in-sync", "DBInstanceIdentifier": "sample-primary" } ], "Port": 3306, "PreferredBackupWindow": "03:34-04:04", "VpcSecurityGroups": [ { "Status": "active", "VpcSecurityGroupId": "sg-ddb65fec" } ], "DBSubnetGroup": "default", "StorageEncrypted": false, "DatabaseName": "sample", "EngineVersion": "5.7.mysql_aurora.2.11.0", "DBClusterParameterGroup": "default.aurora-mysql5.7", "BackupRetentionPeriod": 1, "AvailabilityZones": [ "us-east-1b", "us-east-1c", "us-east-1d" ], "LatestRestorableTime": "2023-03-31T20:06:08.903Z", "PreferredMaintenanceWindow": "wed:08:15-wed:08:45" }, { "Status": "available", "Engine": "aurora-mysql", "Endpoint": "aurora-sample.cluster-123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com", "AllocatedStorage": 1, "DBClusterIdentifier": "aurora-sample-cluster", "MasterUsername": "mymasteruser", "EarliestRestorableTime": "2023-03-30T10:21:34.826Z", "DBClusterMembers": [ { "IsClusterWriter": false, "DBClusterParameterGroupStatus": "in-sync", "DBInstanceIdentifier": "aurora-replica-sample" }, { "IsClusterWriter": true, "DBClusterParameterGroupStatus": "in-sync", "DBInstanceIdentifier": "aurora-sample" } ], "Port": 3306, "PreferredBackupWindow": "10:20-10:50", "VpcSecurityGroups": [ { "Status": "active", "VpcSecurityGroupId": "sg-55da224b" } ], "DBSubnetGroup": "default", "StorageEncrypted": false, "DatabaseName": "sample", "EngineVersion": "5.7.mysql_aurora.2.11.0", "DBClusterParameterGroup": "default.aurora-mysql5.7", "BackupRetentionPeriod": 1, "AvailabilityZones": [ "us-east-1b", "us-east-1c", "us-east-1d" ], "LatestRestorableTime": "2023-03-31T20:00:11.491Z", "PreferredMaintenanceWindow": "sun:03:53-sun:04:23" } ] }
To view DB cluster information using the Amazon RDS API, use the DescribeDBClusters operation.
Viewing DB cluster status
The status of a DB cluster indicates its current operational state. You can view the status of a DB cluster and the cluster instances by using the Amazon RDS console, the Amazon CLI, or the API.
Note
Aurora also uses another status called maintenance status, which is shown in the Maintenance column of the Amazon RDS console. This value indicates the status of any maintenance patches that need to be applied to a DB cluster. Maintenance status is independent of DB cluster status. For more information about maintenance status, see Applying updates to a DB cluster.
Find the possible status values for DB clusters in the following table.
| DB cluster status | Billed | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Available | Billed |
The DB cluster is available for modifications. When an Aurora Serverless cluster is available and paused, you're billed for storage only. |
| Backing-up | Billed |
The DB cluster is currently being backed up. |
| Backtracking | Billed |
The DB cluster is currently being backtracked. This status only applies to Aurora MySQL. |
| Cloning-failed | Not billed |
Cloning a DB cluster failed. |
| Creating | Not billed |
The DB cluster is being created. The DB cluster is inaccessible while it is being created. |
| Deleting | Not billed |
The DB cluster is being deleted. |
| Failing-over | Billed |
A failover from the primary instance to an Aurora Replica is being performed. |
| Inaccessible-encryption-credentials | Not billed |
The Amazon KMS key used to encrypt or decrypt the DB cluster can't be accessed or recovered. |
|
Inaccessible-encryption-credentials-recoverable |
Billed for storage |
The KMS key used to encrypt or decrypt the DB cluster can't be accessed. However, if the KMS key is active, restarting the DB cluster can recover it. For more information, see Encrypting an Amazon Aurora DB cluster. |
| Maintenance | Billed |
Amazon RDS is applying a maintenance update to the DB cluster. This status is used for DB cluster-level maintenance that RDS schedules well in advance. |
| Migrating | Billed |
A DB cluster snapshot is being restored to a DB cluster. |
| Migration-failed | Not billed |
A migration failed. |
| Modifying | Billed |
The DB cluster is being modified because of a customer request to modify the DB cluster. |
| Promoting | Billed |
A read replica is being promoted to a standalone DB cluster. |
| Preparing-data-migration | Billed |
Amazon RDS is preparing to migrate data to Aurora. |
| Renaming | Billed |
The DB cluster is being renamed because of a customer request to rename it. |
| Resetting-master-credentials | Billed |
The master credentials for the DB cluster are being reset because of a customer request to reset them. |
| Starting | Billed for storage |
The DB cluster is starting. |
| Stopped | Billed for storage |
The DB cluster is stopped. |
| Stopping | Billed for storage |
The DB cluster is being stopped. |
| Storage-optimization | Billed |
Your DB instance is being modified to change the storage size or type. The DB instance is fully operational. However, while the status of your DB instance is storage-optimization, you can't request any changes to the storage of your DB instance. The storage optimization process is usually short, but can sometimes take up to and even beyond 24 hours. |
| Update-iam-db-auth | Billed |
IAM authorization for the DB cluster is being updated. |
| Upgrading | Billed |
The DB cluster engine or operating system version is being upgraded. |
|
upgrade_failed |
Not billed |
The DB cluster has failed to upgrade to a supported version. Aurora creates a final snapshot with the prefix |
To view the status of a DB cluster
Sign in to the Amazon Web Services Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
The Databases page appears with the list of DB clusters. For each DB cluster, the status value is displayed.
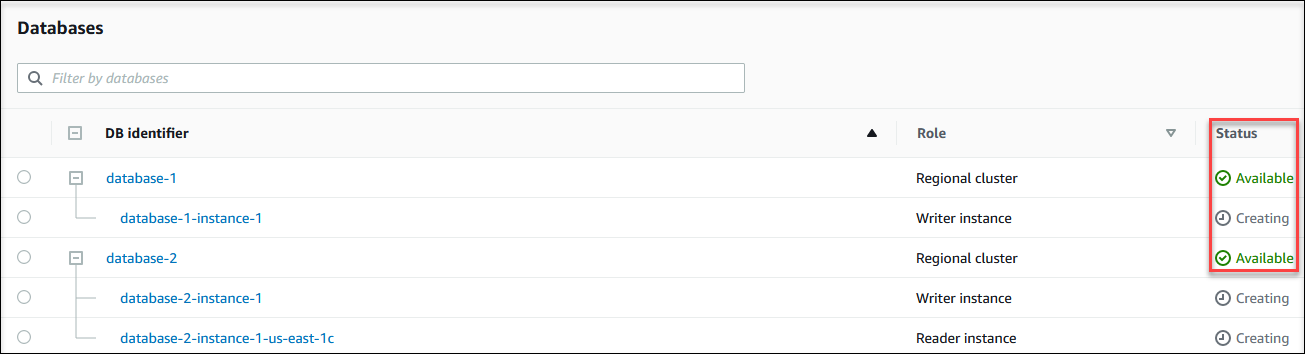
To view just the status of the DB clusters, use the following query in Amazon CLI.
aws rds describe-db-clusters --query 'DBClusters[*].[DBClusterIdentifier,Status]' --output table
Viewing DB instance status in an Aurora cluster
The status of a DB instance in an Aurora cluster indicates its current operational state. You can use the following procedures to view the DB instance status of a cluster in the Amazon RDS console, the Amazon CLI command, or the API operation.
Note
Amazon RDS also uses another status called maintenance status, which is shown in the Maintenance column of the Amazon RDS console. This value indicates the status of any maintenance patches that need to be applied to a DB instance. Maintenance status is independent of DB instance status. For more information about maintenance status, see Applying updates to a DB cluster.
Find the possible status values for DB instances in the following table. This table also shows whether you will be billed for the DB instance and storage, billed only for storage, or not billed. For all DB instance statuses, you are always billed for backup usage.
| DB instance status | Billed | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
available |
Billed |
The DB instance is available for modifications. |
|
backing-up |
Billed |
The DB instance is currently being backed up. |
| backtracking |
Billed |
The DB instance is currently being backtracked. This status only applies to Aurora MySQL. |
|
configuring-enhanced-monitoring |
Billed |
Enhanced Monitoring is being enabled or disabled for this DB instance. |
|
configuring-iam-database-auth |
Billed |
Amazon Identity and Access Management (IAM) database authentication is being enabled or disabled for this DB instance. |
|
configuring-log-exports |
Billed |
Publishing log files to Amazon CloudWatch Logs is being enabled or disabled for this DB instance. |
|
converting-to-vpc |
Billed |
The DB instance is being converted from a DB instance that is not in an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) to a DB instance that is in an Amazon VPC. |
|
creating |
Not billed (non-PITR) Billed (PITR only) |
The DB instance is being created. The DB instance is inaccessible while it is being created. If you restore a database during point-in-time recovery (PITR), you're billed while the database is in the creating state. This is the only scenario in which the creating state incurs charges. |
|
delete-precheck |
Not billed |
Amazon RDS is validating that read replicas are safe to delete. |
|
deleting |
Not billed |
The DB instance is being deleted. |
|
failed |
Not billed |
The DB instance has failed and Amazon RDS can't recover it. Perform a point-in-time restore to the latest restorable time of the DB instance to recover the data. |
|
inaccessible-encryption-credentials |
Not billed |
The Amazon KMS key used to encrypt or decrypt the DB instance can't be accessed or recovered. |
|
inaccessible-encryption-credentials-recoverable |
Billed for storage |
The KMS key used to encrypt or decrypt the DB instance can't be accessed. However, if the KMS key is active, restarting the DB instance can recover it. For more information, see Encrypting an Amazon Aurora DB cluster. |
|
incompatible-create |
Not billed |
Amazon RDS is attempting to create a DB instance but can't do so because resources are incompatible with your DB instance. This status can occur if, for example, the instance profile for your DB instance doesn't have the correct permissions. |
|
incompatible-network |
Not billed |
Amazon RDS is attempting to perform a recovery action on a DB instance but can't do so because the VPC is in a state that prevents the action from being completed. This status can occur if, for example, all available IP addresses in a subnet are in use and Amazon RDS can't get an IP address for the DB instance. |
|
incompatible-option-group |
Billed |
Amazon RDS attempted to apply an option group change but can't do so, and Amazon RDS can't roll back to the previous option group state. For more information, check the Recent Events list for the DB instance. This status can occur if, for example, the option group contains an option such as TDE and the DB instance doesn't contain encrypted information. |
|
incompatible-parameters |
Billed |
Amazon RDS can't start the DB instance because the parameters specified in the DB instance's DB parameter group aren't compatible with the DB instance. Revert the parameter changes or make them compatible with the DB instance to regain access to your DB instance. For more information about the incompatible parameters, check the Recent Events list for the DB instance. |
|
incompatible-restore |
Not billed |
Amazon RDS can't do a point-in-time restore. Common causes for this status include using temp tables or using MyISAM tables with MySQL. |
| insufficient-capacity |
Not billed |
Amazon RDS can't create your instance because sufficient capacity isn't currently available. To create your DB instance in the same AZ with the same instance type, delete your DB instance, wait a few hours, and try to create again. Alternatively, create a new instance using a different instance class or AZ. |
|
maintenance |
Billed |
Amazon RDS is applying a maintenance update to the DB instance. This status is used for instance-level maintenance that RDS schedules well in advance. |
|
modifying |
Billed |
The DB instance is being modified because of a customer request to modify the DB instance. |
|
moving-to-vpc |
Billed |
The DB instance is being moved to a new Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC). |
|
rebooting |
Billed |
The DB instance is being rebooted because of a customer request or an Amazon RDS process that requires the rebooting of the DB instance. |
|
resetting-master-credentials |
Billed |
The master credentials for the DB instance are being reset because of a customer request to reset them. |
|
renaming |
Billed |
The DB instance is being renamed because of a customer request to rename it. |
|
restore-error |
Billed |
The DB instance encountered an error attempting to restore to a point-in-time or from a snapshot. |
|
starting |
Billed for storage |
The DB instance is starting. |
|
stopped |
Billed for storage |
The DB instance is stopped. |
|
stopping |
Billed for storage |
The DB instance is being stopped. |
|
storage-config-upgrade |
Billed |
The storage file system configuration of the DB instance is being upgraded. This status only applies to green databases within a blue/green deployment, or to DB instance read replicas. |
|
storage-full |
Billed |
The DB instance has reached its storage capacity allocation. This is a critical status, and we recommend that you fix this issue immediately. To do so, scale up your storage by modifying the DB instance. To avoid this situation, set Amazon CloudWatch alarms to warn you when storage space is getting low. |
| storage-initialization |
Billed |
The DB instance is loading data blocks from Amazon S3 to optimize volume performance after being restored from a snapshot. It remains available for operations, but performance mights not be at its fullest until initialization completes. |
|
storage-optimization |
Billed |
Amazon RDS is optimizing the storage of your DB instance. The storage optimization process is usually short, but can sometimes take up to and even beyond 24 hours. During storage optimization, the DB instance remains available. Storage optimization is a background process that doesn't affect the instance's availability. |
|
upgrading |
Billed |
The database engine or operating system version is being upgraded. |
|
upgrade_failed |
Not billed |
The DB instance has failed to upgrade to a supported version. Aurora creates a final snapshot with the prefix |
To view the status of a DB instance
Sign in to the Amazon Web Services Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
The Databases page appears with the list of DB instances. For each DB instance in a cluster, the status value is displayed.
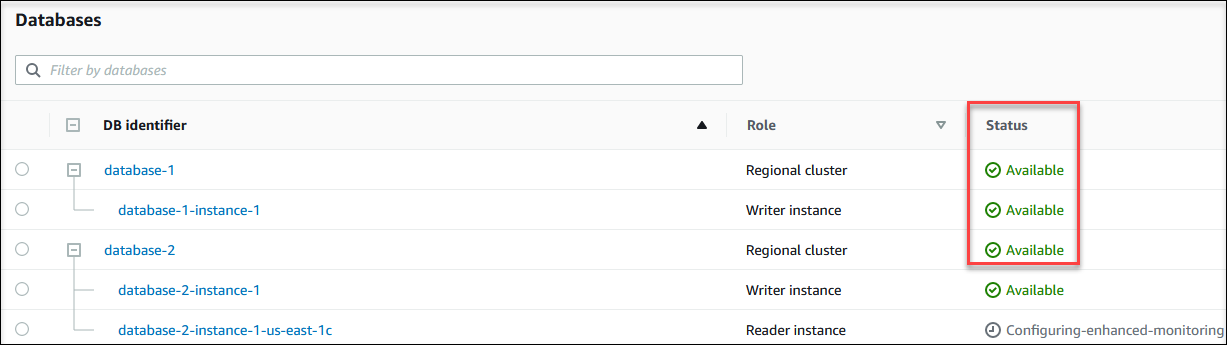
To view DB instance and its status information by using the Amazon CLI, use the describe-db-instances command. For example, the following Amazon CLI command lists all the DB instances information .
aws rds describe-db-instances
To view a specific DB instance and its status, call the describe-db-instances command with the following option:
-
DBInstanceIdentifier– The name of the DB instance.
aws rds describe-db-instances --db-instance-identifiermydbinstance
To view just the status of all the DB instances, use the following query in Amazon CLI.
aws rds describe-db-instances --query 'DBInstances[*].[DBInstanceIdentifier,DBInstanceStatus]' --output table
To view the status of the DB instance using the Amazon RDS API, call the DescribeDBInstances operation.