Switching a blue/green deployment in Amazon RDS
A switchover transitions the green environment to be the new production environment. When the green DB instance has read replicas, they are also transitioned. Before you switch over, production traffic is routed to the DB instance and read replicas in the blue environment. After you switch over, production traffic is routed to the DB instance and read replicas in the green environment.
Switching over a blue/green deployment is not the same as promoting the green DB instance within the blue/green deployment. If you manually promote the green DB instance by choosing Promote from the Actions menu, replication between the blue and green environments breaks and the blue/green deployment enters a state of Invalid configuration.
Topics
Switchover timeout
You can specify a switchover timeout period between 30 seconds and 3,600 seconds (one hour). If the switchover takes longer than the specified duration, then any changes are rolled back and no changes are made to either environment. The default timeout period is 300 seconds (five minutes).
Switchover guardrails
When you start a switchover, Amazon RDS runs some basic checks to test the readiness of the blue and green environments for switchover. These checks are known as switchover guardrails. These switchover guardrails prevent a switchover if the environments aren't ready for it. Therefore, they avoid longer than expected downtime and prevent the loss of data between the blue and green environments that might result if the switchover started.
Amazon RDS runs the following guardrail checks on the green environment:
-
Replication health – Checks if green primary DB instance replication status is healthy. The green primary DB instance is a replica of the blue primary DB instance.
-
Replication lag – Checks if the replica lag of the green primary DB instance is within allowable limits for switchover. The allowable limits are based on the specified timeout period. Replica lag indicates how far the green primary DB instance is lagging behind its blue primary DB instance. For more information, see Monitoring replica lag prior to switchover.
-
Active writes – Makes sure there are no active writes on the green primary DB instance.
Amazon RDS runs the following guardrail checks on the blue environment:
-
External replication – For RDS for PostgreSQL, makes sure that the blue environment isn't a self-managed logical source (publisher) or replica (subscriber). If it is, we recommend that you drop the self-managed replication slots and subscriptions across all databases in the blue environment, proceed with switchover, then recreate them to resume replication. For RDS for MySQL and RDS for MariaDB, checks whether the blue database isn't an external binlog replica. If it is, make sure that it is not actively replicating.
-
Long-running active writes – Makes sure there are no long-running active writes on the blue primary DB instance because they can increase replica lag.
-
Long-running DDL statements – Makes sure there are no long-running DDL statements on the blue primary DB instance because they can increase replica lag.
-
Unsupported PostgreSQL changes – For RDS for PostgreSQL blue/green deployments that use logical replication, makes sure that no DDL changes and no additions or modifications of large objects have been performed on the blue environment. For more information, see Logical replication-specific limitations for blue/green deployments.
If Amazon RDS detects unsupported PostgreSQL changes, it changes the replication state to
Replication degradedand notifies you that switchover is not available for the blue/green deployment. To proceed with switchover, we recommend that you delete and recreate the blue/green deployment and all green databases. To do so, choose Actions, Delete with green databases.
Switchover actions
When you switch over a blue/green deployment, RDS performs the following actions:
-
Runs guardrail checks to verify if the blue and green environments are ready for switchover.
-
Stops new write operations on the primary DB instance in both environments.
-
Drops connections to the DB instances in both environments and doesn't allow new connections.
-
Waits for replication to catch up in the green environment so that the green environment is in sync with the blue environment.
-
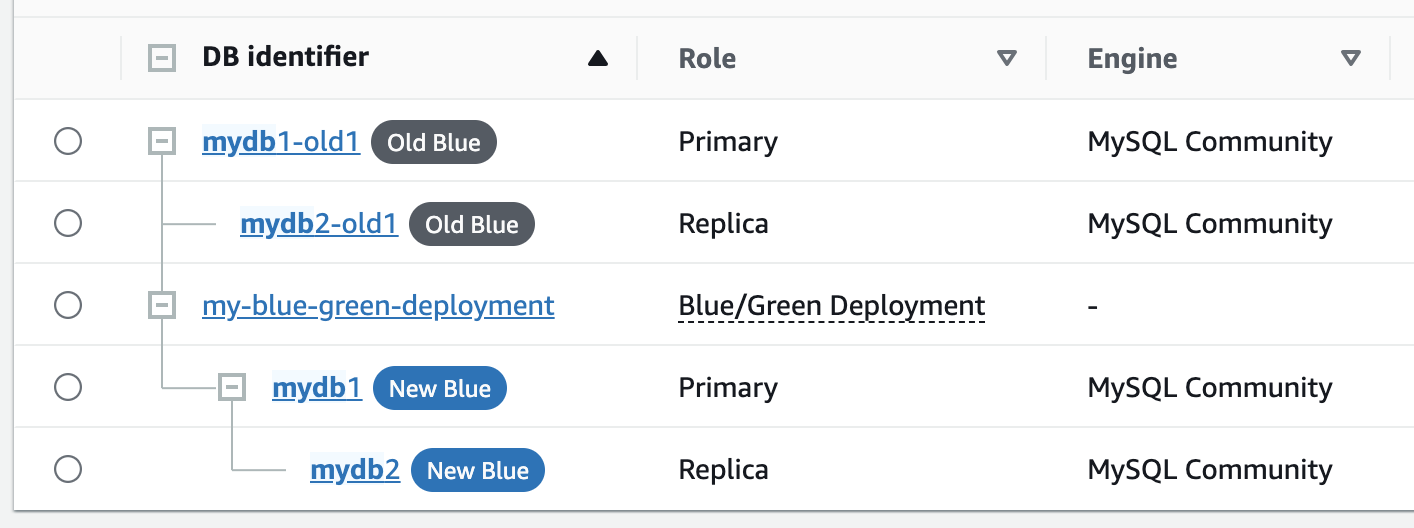
Renames the DB instances in the both environments.
RDS renames the DB instances in the green environment to match the corresponding DB instances in the blue environment. For example, assume the name of a DB instance in the blue environment is
mydb. Also assume the name of the corresponding DB instance in the green environment ismydb-green-abc123. During switchover, the name of the DB instance in the green environment is changed tomydb.RDS renames the DB instances in the blue environment by appending
-oldto the current name, wherennmydb. After switchover, the DB instance name might bemydb-old1.RDS also renames the endpoints in the green environment to match the corresponding endpoints in the blue environment so that application changes aren't required.
-
Allows connections to databases in both environments.
-
Allows write operations on the primary DB instance in the new production environment.
After switchover, the previous production primary DB instance only allows read operations until you set the
read_onlyparameter (for RDS for MySQL) or thedefault_transaction_read_onlyparameter (for RDS for PostgreSQL) to0and reboot the DB instance.
You can monitor the status of a switchover using Amazon EventBridge. For more information, see Blue/green deployment events.
During switchover, tags from the blue environment replace all tags on resources in the green environment. Any tags that you added directly to green environment resources are overwritten during this process. For more information about tags, see Tagging Amazon RDS resources.
If the switchover starts and then stops before finishing for any reason, then any changes are rolled back, and no changes are made to either environment.
Switchover best practices
Before you switch over, we strongly recommend that you adhere to best practices by completing the following tasks:
-
Thoroughly test the resources in the green environment. Make sure they function properly and efficiently.
-
Monitor relevant Amazon CloudWatch metrics. For more information, see Verifying CloudWatch metrics before switchover.
-
Identify the best time for the switchover.
During the switchover, writes are cut off from databases in both environments. Identify a time when traffic is lowest on your production environment. Long-running transactions, such as active DDLs, can increase your switchover time, resulting in longer downtime for your production workloads.
If there's a large number of connections on your DB instances, consider manually reducing them to the minimum amount necessary for your application before you switch over the blue/green deployment. One way to achieve this is to create a script that monitors the status of the blue/green deployment and starts cleaning up connections when it detects that the status has changed to
SWITCHOVER_IN_PROGRESS. -
Make sure the DB instances in both environments are in
Availablestate. -
Make sure the primary DB instance in the green environment is healthy and replicating.
-
Make sure that your network and client configurations don’t increase the DNS cache Time-To-Live (TTL) beyond five seconds, which is the default for RDS DNS zones. Otherwise, applications will continue to send write traffic to the blue environment after switchover.
-
Make sure data loading is complete before switching over. For more information, see Lazy loading and storage initialization for blue/green deployments.
-
For RDS for PostgreSQL blue/green deployments that use logical replication, do the following:
-
Review the logical replication limitations and take any required actions prior to switchover. For more information, see Logical replication-specific limitations for blue/green deployments.
-
Run the
ANALYZEoperation to refresh thepg_statisticstable. This reduces the risk of performance issues after switchover.
-
Note
During a switchover, you can't modify any DB instances included in the switchover.
Verifying CloudWatch metrics before switchover
Before you switch over a blue/green deployment, we recommend that you check the value of the following metric within Amazon CloudWatch.
-
DatabaseConnections– Use this metric to estimate the level of activity on the blue/green deployment, and make sure that the value is at an acceptable level for your deployment before you switch over. If Performance Insights is turned on,DBLoadis a more accurate metric.
For more information, see Amazon CloudWatch metrics for Amazon RDS.
Monitoring replica lag prior to switchover
Before you switch over a blue/green deployment, make sure that replica lag is close to zero in order to reduce downtime.
RDS for MySQL and RDS for MariaDB
For MySQL and MariaDB blue/green deployments,
check the ReplicaLag CloudWatch metric in the green
environment to identify the current replica lag. For more information, see Diagnosing and resolving lag
between read replicas.
RDS for PostgreSQL
For PostgreSQL blue/green deployments that use physical replication, see Monitoring and tuning the replication process for instructions to identify the current replica lag.
For PostgreSQL blue/green deployments that use logical
replication, check the OldestReplicationSlotLag CloudWatch metric in the
blue environment to identify the current replica lag. For more information, see Amazon CloudWatch instance-level metrics for Amazon RDS.
In addition, you can run the following SQL query in the blue environment:
SELECT slot_name, confirmed_flush_lsn as flushed, pg_current_wal_lsn(), (pg_current_wal_lsn() - confirmed_flush_lsn) AS lsn_distance FROM pg_catalog.pg_replication_slots WHERE slot_type = 'logical'; slot_name | flushed | pg_current_wal_lsn | lsn_distance -----------------+---------------+--------------------+------------ logical_replica1 | 47D97/CF32980 | 47D97/CF3BAC8 | 37192
The confirmed_flush_lsn represents the last log sequence number (LSN) that
was sent to the replica. The pg_current_wal_lsn represents where the database
is now. An lsn_distance of 0 means that the replica is caught up.
For an explanation of when blue/green deployments use physical replication versus logical replication, see PostgreSQL replication methods for blue/green deployments.
Switching over a blue/green deployment
You can switch over a blue/green deployment using the Amazon Web Services Management Console, the Amazon CLI, or the RDS API.
To switch over a blue/green deployment
Sign in to the Amazon Web Services Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.amazonaws.cn/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases, and then choose the blue/green deployment that you want to switch over.
-
For Actions, choose Switch over.
The Switch over page appears.
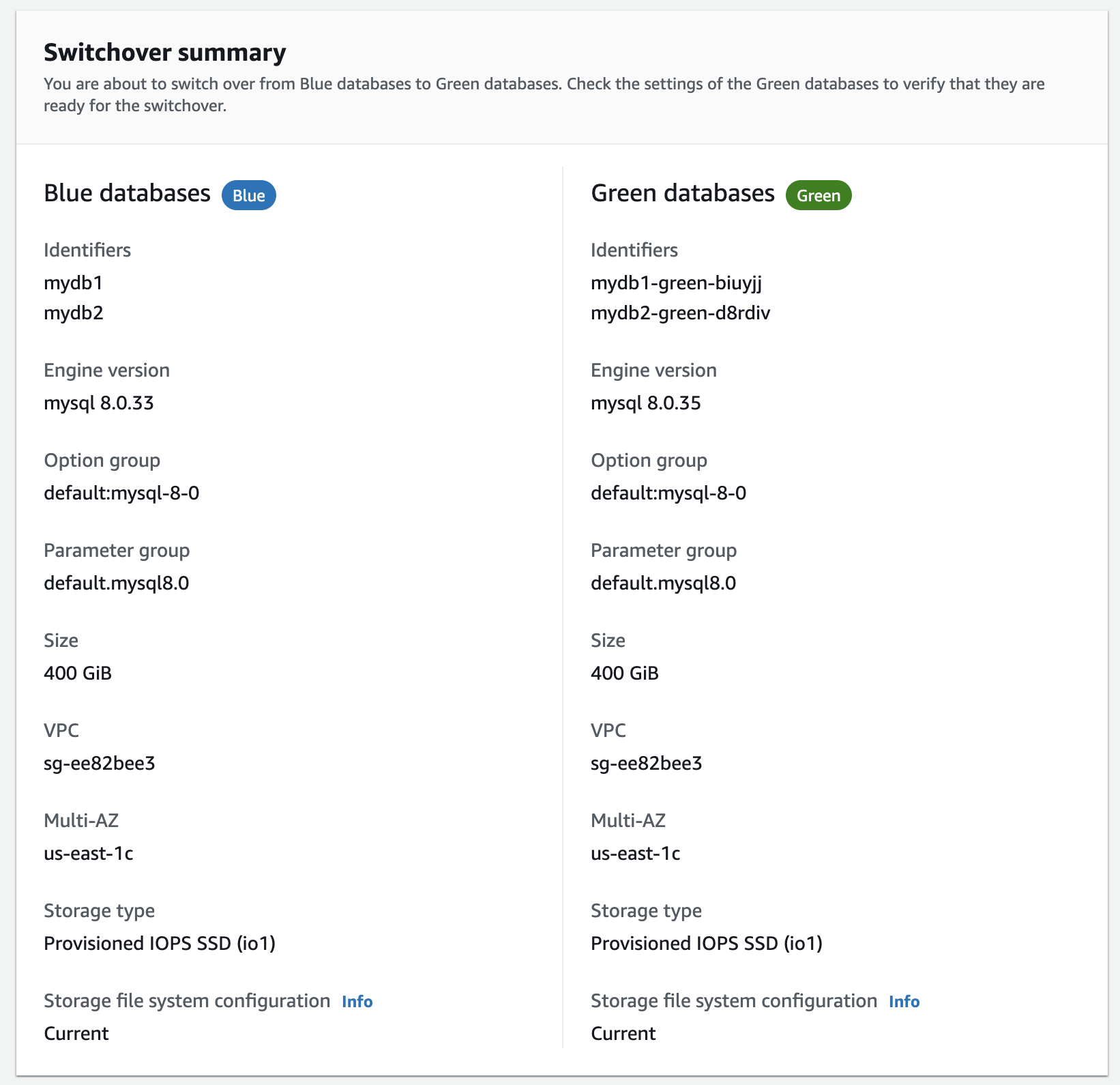
-
On the Switch over page, review the switchover summary. Make sure the resources in both environments match what you expect. If they don't, choose Cancel.
-
For Timeout settings, enter the time limit for switchover.
-
If your instance is running RDS for PostgreSQL, review and acknowledge the pre-switchover recommendations. For more information, see Logical replication-specific limitations for blue/green deployments.
-
Choose Switch over.
To switch over a blue/green deployment by using the Amazon CLI, use the switchover-blue-green-deployment command with the following options:
-
--blue-green-deployment-identifier– Specify the resource ID of the blue/green deployment. -
--switchover-timeout– Specify the time limit for the switchover, in seconds. The default is 300.
Example Switch over a blue/green deployment
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds switchover-blue-green-deployment \ --blue-green-deployment-identifierbgd-1234567890abcdef\ --switchover-timeout600
For Windows:
aws rds switchover-blue-green-deployment ^ --blue-green-deployment-identifierbgd-1234567890abcdef^ --switchover-timeout600
To switch over a blue/green deployment by using the Amazon RDS API, use the SwitchoverBlueGreenDeployment operation with the following parameters:
-
BlueGreenDeploymentIdentifier– Specify the resource ID of the blue/green deployment. -
SwitchoverTimeout– Specify the time limit for the switchover, in seconds. The default is 300.
After switchover
After a switchover, the DB instances in the previous blue environment are retained. Standard costs apply to these resources. Replication between the blue and green environments stops.
RDS renames the DB instances in the blue environment by appending
-old to the current resource name, where
nnread_only
parameter (for RDS for MySQL) or the default_transaction_read_only parameter (for
RDS for PostgreSQL) to 0.
RDS names the DB instances in the green environment
-new.n
If you delete the blue/green deployment resource, RDS retains the
-old and
n-new resources.n
Updating the parent node for consumers
RDS offers fully managed read replicas. However, it also provides the option to set up self-managed replicas, also known as external replicas. External replicas allow you to use third-party resources as replication targets.
After you switch over an RDS for MariaDB or RDS for MySQL blue/green deployment, if the blue DB instance had any external replicas or binary log consumers prior to switchover, you must update their parent node after switchover in order to maintain replication continuity.
To update the parent node
-
After switchover, the DB instance that was previously in the green environment emits an event that contains the master log file name and master log position. To locate the event, navigate to the RDS console and choose Events from the left navigation pane.
-
Filter by events where the source is the name of the old green DB instance, before switchover.
-
Locate the event that contains the binary log coordinates. The event message is similar to:
Binary log coordinates in green environment after switchover: file mysql-bin-changelog..000003and position40134574 -
Make sure that the consumer or replica has applied all binary logs from the old blue environment. Then, use the provided binary log coordinates to resume replication on the consumers. For example, if you're running a MySQL replica on EC2, you can use the following commands:
MySQL 8.0.22 and lower major and minor versions
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='{new-writer-endpoint}', MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin-changelog.000003', MASTER_LOG_POS=40134574;MySQL 8.0.23 and higher major and minor versions
CHANGE REPLICATION SOURCE TO SOURCE_HOST='{new-writer-endpoint}', SOURCE_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin-changelog.000003', SOURCE_LOG_POS=40134574;
If the consumer is another RDS for MySQL or RDS for MariaDB DB instance, run the following stored procedures in order:
-
mysql.rds_reset_external_master (for version 8.0 and lower) or mysql_rds_reset_external_source (for version 8.4 and higher)
-
mysql.rds_set_external_master (for version 8.0 and lower) or mysql_rds_set_external_source (for version 8.4 and higher)