Managing throughput capacity automatically with DynamoDB auto scaling
Many database workloads are cyclical in nature, while others are difficult to predict in advance. For one example, consider a social networking app where most of the users are active during daytime hours. The database must be able to handle the daytime activity, but there's no need for the same levels of throughput at night. For another example, consider a new mobile gaming app that is experiencing unexpectedly rapid adoption. If the game becomes too popular it could exceed the available database resources, resulting in slow performance and unhappy customers. These kinds of workloads often require manual intervention to scale database resources up or down in response to varying usage levels.
Amazon DynamoDB auto scaling uses the Amazon Application Auto Scaling service to dynamically adjust provisioned throughput capacity on your behalf, in response to actual traffic patterns. This enables a table or a global secondary index (GSI) to increase its provisioned read and write capacity to handle sudden increases in traffic, without throttling. When the workload decreases, Application Auto Scaling decreases the throughput so that you don't pay for unused provisioned capacity.
Note
If you use the Amazon Web Services Management Console to create a table or a global secondary index, DynamoDB auto scaling is enabled by default. You can modify your auto scaling settings at any time. For more information, see Using the Amazon Web Services Management Console with DynamoDB auto scaling.
When you delete a table or global table replica then any associated scalable targets, scaling polices, or CloudWatch alarms are not automatically deleted with it.
With Application Auto Scaling, you create a scaling policy for a table or a global secondary index. The scaling policy specifies whether you want to scale read capacity or write capacity (or both), and the minimum and maximum provisioned capacity unit settings for the table or index.
The scaling policy also contains a target utilization—the percentage of consumed provisioned throughput at a point in time. Application Auto Scaling uses a target tracking algorithm to adjust the provisioned throughput of the table (or index) upward or downward in response to actual workloads, so that the actual capacity utilization remains at or near your target utilization.
DynamoDB outputs consumed provisioned throughput for one-minute periods. Auto scaling triggers when your consumed capacity breaches the configured target utilization for two consecutive minutes. CloudWatch alarms might have a short delay of up to a few minutes before triggering auto scaling. This delay ensures accurate CloudWatch metric evaluation. If the consumed throughput spikes are more than a minute apart, auto scaling might not trigger. Similarly, a scale down event can occur when 15 consecutive data points are lower than the target utilization. In either case, after auto scaling triggers, the UpdateTable API is invoked. It then takes several minutes to update the provisioned capacity for the table or index. During this period, any requests that exceed the previous provisioned capacity of the tables are throttled.
Important
You can't adjust the number of data points to breach to trigger the underlying alarm (though the current number could change in the future).
You can set the auto scaling target utilization values between 20 and 90 percent for your read and write capacity.
Note
In addition to tables, DynamoDB auto scaling also supports global secondary indexes. Every global secondary index has its own provisioned throughput capacity, separate from that of its base table. When you create a scaling policy for a global secondary index, Application Auto Scaling adjusts the provisioned throughput settings for the index to ensure that its actual utilization stays at or near your desired utilization ratio.
How DynamoDB auto scaling works
Note
To get started quickly with DynamoDB auto scaling, see Using the Amazon Web Services Management Console with DynamoDB auto scaling.
The following diagram provides a high-level overview of how DynamoDB auto scaling manages throughput capacity for a table.
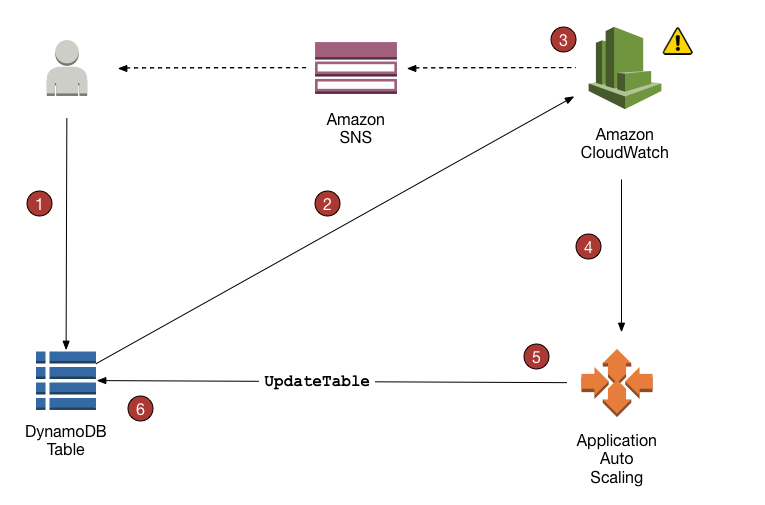
The following steps summarize the auto scaling process as shown in the previous diagram:
-
You create an Application Auto Scaling policy for your DynamoDB table.
-
DynamoDB publishes consumed capacity metrics to Amazon CloudWatch.
-
If the table's consumed capacity exceeds your target utilization (or falls below the target) for a specific length of time, Amazon CloudWatch triggers an alarm. You can view the alarm on the console and receive notifications using Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS).
-
The CloudWatch alarm invokes Application Auto Scaling to evaluate your scaling policy.
-
Application Auto Scaling issues an
UpdateTablerequest to adjust your table's provisioned throughput. -
DynamoDB processes the
UpdateTablerequest, dynamically increasing (or decreasing) the table's provisioned throughput capacity so that it approaches your target utilization.
To understand how DynamoDB auto scaling works, suppose that you have a table named
ProductCatalog. The table is bulk-loaded with data infrequently, so it
doesn't incur very much write activity. However, it does experience a high degree of
read activity, which varies over time. By monitoring the Amazon CloudWatch metrics for
ProductCatalog, you determine that the table requires 1,200 read
capacity units (to avoid DynamoDB throttling read requests when activity is at its peak).
You also determine that ProductCatalog requires 150 read capacity units at
a minimum, when read traffic is at its lowest point. For more information about
preventing throttling, see Troubleshooting throttling in Amazon DynamoDB.
Within the range of 150 to 1,200 read capacity units, you decide that a target
utilization of 70 percent would be appropriate for the ProductCatalog
table. Target utilization is the ratio of consumed capacity units
to provisioned capacity units, expressed as a percentage. Application Auto Scaling uses its target
tracking algorithm to ensure that the provisioned read capacity of
ProductCatalog is adjusted as required so that utilization remains at
or near 70 percent.
Note
DynamoDB auto scaling modifies provisioned throughput settings only when the actual workload stays elevated or depressed for a sustained period of several minutes. The Application Auto Scaling target tracking algorithm seeks to keep the target utilization at or near your chosen value over the long term.
Sudden, short-duration spikes of activity are accommodated by the table's built-in burst capacity. For more information, see Burst capacity.
To enable DynamoDB auto scaling for the ProductCatalog table, you create a
scaling policy. This policy specifies the following:
-
The table or global secondary index that you want to manage
-
Which capacity type to manage (read capacity or write capacity)
-
The upper and lower boundaries for the provisioned throughput settings
-
Your target utilization
When you create a scaling policy, Application Auto Scaling creates a pair of Amazon CloudWatch alarms on your behalf. Each pair represents the upper and lower boundaries for your provisioned throughput settings. These CloudWatch alarms are triggered when the table's actual utilization deviates from your target utilization for a sustained period of time.
When one of the CloudWatch alarms is triggered, Amazon SNS sends you a notification (if you have
enabled it). The CloudWatch alarm then invokes Application Auto Scaling, which in turn notifies DynamoDB to
adjust the ProductCatalog table's provisioned capacity upward or downward
as appropriate.
During a scaling event, Amazon Config is charged per configuration item recorded. When a scaling event occurs, four CloudWatch alarms are created for each read and write auto-scaling event: ProvisionedCapacity alarms: ProvisionedCapacityLow, ProvisionedCapacityHigh and ConsumedCapacity alarms: AlarmHigh, AlarmLow. This results in a total of eight alarms. Therefore, Amazon Config records eight configuration items for every scaling event.
Note
You can also schedule your DynamoDB scaling so it happens at certain times. Learn the basic steps here.
Usage notes
Before you begin using DynamoDB auto scaling, you should be aware of the following:
-
DynamoDB auto scaling can increase read capacity or write capacity as often as necessary, in accordance with your auto scaling policy. All DynamoDB quotas remain in effect, as described in Quotas in Amazon DynamoDB.
-
DynamoDB auto scaling doesn't prevent you from manually modifying provisioned throughput settings. These manual adjustments don't affect any existing CloudWatch alarms that are related to DynamoDB auto scaling.
-
If you enable DynamoDB auto scaling for a table that has one or more global secondary indexes, we highly recommend that you also apply auto scaling uniformly to those indexes. This will help ensure better performance for table writes and reads, and help avoid throttling. You can enable auto scaling by selecting Apply same settings to global secondary indexes in the Amazon Web Services Management Console. For more information, see Enabling DynamoDB auto scaling on existing tables.
-
When you delete a table or global table replica, any associated scalable targets, scaling polices or CloudWatch alarms are not automatically deleted with it.
-
When creating a GSI for an existing table, auto scaling is not enabled for the GSI. You will have to manually manage the capacity while the GSI is being built. Once the backfill on the GSI completes and it reaches active status, auto scaling will operate as normal.