Secure Sockets library
Important
This library is hosted on the Amazon-FreeRTOS repository which is deprecated. We recommend that you start here when you create a new project. If you already have an existing FreeRTOS project based on the now deprecated Amazon-FreeRTOS repository, see the Amazon-FreeRTOS Github Repository Migration Guide.
Overview
You can use the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library to create embedded applications that communicate securely. The library is designed to make onboarding easy for software developers from various network programming backgrounds.
The FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library is based on the Berkeley sockets interface, with an additional secure
communication option by TLS protocol. For information about the differences between the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets
library and the Berkeley sockets interface, see SOCKETS_SetSockOpt in the Secure Sockets API
Reference.
Note
Currently, only client APIs, plus a lightweight IP
(lwIP)Bind API, are supported for FreeRTOS Secure
Sockets.
Dependencies and requirements
The FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library depends on a TCP/IP stack and on a TLS implementation. Ports for FreeRTOS meet these dependencies in one of three ways:
-
A custom implementation of both TCP/IP and TLS
-
A custom implementation of TCP/IP, and the FreeRTOS TLS layer with mbedTLS
-
FreeRTOS+TCP
and the FreeRTOS TLS layer with mbedTLS
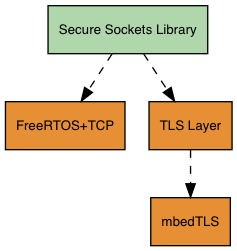
The dependency diagram below shows the reference implementation included with the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library. This reference implementation supports TLS and TCP/IP over Ethernet and Wi-Fi with FreeRTOS+TCP and mbedTLS as dependencies. For more information about the FreeRTOS TLS layer, see Transport Layer Security.
Features
FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library features include:
-
A standard, Berkeley Sockets-based interface
-
Thread-safe APIs for sending and receiving data
-
Easy-to-enable TLS
Troubleshooting
Error codes
The error codes that the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library returns are negative values. For more information about each error code, see Secure Sockets Error Codes in the Secure Sockets API Reference.
Note
If the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets API returns an error code, the coreMQTT library, which depends on the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library, returns the
error code AWS_IOT_MQTT_SEND_ERROR.
Developer support
The FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library includes two helper macros for handling IP addresses:
SOCKETS_inet_addr_quick-
This macro converts an IP address that is expressed as four separate numeric octets into an IP address that is expressed as a 32-bit number in network-byte order.
SOCKETS_inet_ntoa-
This macro converts an IP address that is expressed as a 32-bit number in network byte order to a string in decimal-dot notation.
Usage restrictions
Only TCP sockets are supported by the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library. UDP sockets are not supported.
Server APIs are not supported by the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library, except for a lightweight IP (lwIP)Bind API. Client APIs are supported.
Initialization
To use the FreeRTOS Secure Sockets library, you need to initialize the library and its dependencies. To initialize the Secure Sockets library, use the following code in your application:
BaseType_t xResult = pdPASS; xResult = SOCKETS_Init();
Dependent libraries must be initialized separately. For example, if FreeRTOS+TCP is a dependency, you need to invoke
FreeRTOS_IPInit
API reference
For a full API reference, see Secure Sockets API Reference.
Example usage
The following code connects a client to a server.
#include "aws_secure_sockets.h" #define configSERVER_ADDR0 127 #define configSERVER_ADDR1 0 #define configSERVER_ADDR2 0 #define configSERVER_ADDR3 1 #define configCLIENT_PORT 443 /* Rx and Tx timeouts are used to ensure the sockets do not wait too long for * missing data. */ static const TickType_t xReceiveTimeOut = pdMS_TO_TICKS( 2000 ); static const TickType_t xSendTimeOut = pdMS_TO_TICKS( 2000 ); /* PEM-encoded server certificate */ /* The certificate used below is one of the Amazon Root CAs.\ Change this to the certificate of your choice. */ static const char cTlsECHO_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_PEM[] = "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n" "MIIBtjCCAVugAwIBAgITBmyf1XSXNmY/Owua2eiedgPySjAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjA5\n" "MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEPMA0GA1UEChMGQW1hem9uMRkwFwYDVQQDExBBbWF6b24g\n" "Um9vdCBDQSAzMB4XDTE1MDUyNjAwMDAwMFoXDTQwMDUyNjAwMDAwMFowOTELMAkG\n" "A1UEBhMCVVMxDzANBgNVBAoTBkFtYXpvbjEZMBcGA1UEAxMQQW1hem9uIFJvb3Qg\n" "Q0EgMzBZMBMGByqGSM49AgEGCCqGSM49AwEHA0IABCmXp8ZBf8ANm+gBG1bG8lKl\n" "ui2yEujSLtf6ycXYqm0fc4E7O5hrOXwzpcVOho6AF2hiRVd9RFgdszflZwjrZt6j\n" "QjBAMA8GA1UdEwEB/wQFMAMBAf8wDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgGGMB0GA1UdDgQWBBSr\n" "ttvXBp43rDCGB5Fwx5zEGbF4wDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNJADBGAiEA4IWSoxe3jfkr\n" "BqWTrBqYaGFy+uGh0PsceGCmQ5nFuMQCIQCcAu/xlJyzlvnrxir4tiz+OpAUFteM\n" "YyRIHN8wfdVoOw==\n" "-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n"; static const uint32_t ulTlsECHO_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_LENGTH = sizeof( cTlsECHO_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_PEM ); void vConnectToServerWithSecureSocket( void ) { Socket_t xSocket; SocketsSockaddr_t xEchoServerAddress; BaseType_t xTransmitted, lStringLength; xEchoServerAddress.usPort = SOCKETS_htons( configCLIENT_PORT ); xEchoServerAddress.ulAddress = SOCKETS_inet_addr_quick( configSERVER_ADDR0, configSERVER_ADDR1, configSERVER_ADDR2, configSERVER_ADDR3 ); /* Create a TCP socket. */ xSocket = SOCKETS_Socket( SOCKETS_AF_INET, SOCKETS_SOCK_STREAM, SOCKETS_IPPROTO_TCP ); configASSERT( xSocket != SOCKETS_INVALID_SOCKET ); /* Set a timeout so a missing reply does not cause the task to block indefinitely. */ SOCKETS_SetSockOpt( xSocket, 0, SOCKETS_SO_RCVTIMEO, &xReceiveTimeOut, sizeof( xReceiveTimeOut ) ); SOCKETS_SetSockOpt( xSocket, 0, SOCKETS_SO_SNDTIMEO, &xSendTimeOut, sizeof( xSendTimeOut ) ); /* Set the socket to use TLS. */ SOCKETS_SetSockOpt( xSocket, 0, SOCKETS_SO_REQUIRE_TLS, NULL, ( size_t ) 0 ); SOCKETS_SetSockOpt( xSocket, 0, SOCKETS_SO_TRUSTED_SERVER_CERTIFICATE, cTlsECHO_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_PEM, ulTlsECHO_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_LENGTH ); if( SOCKETS_Connect( xSocket, &xEchoServerAddress, sizeof( xEchoServerAddress ) ) == 0 ) { /* Send the string to the socket. */ xTransmitted = SOCKETS_Send( xSocket, /* The socket receiving. */ ( void * )"some message", /* The data being sent. */ 12, /* The length of the data being sent. */ 0 ); /* No flags. */ if( xTransmitted < 0 ) { /* Error while sending data */ return; } SOCKETS_Shutdown( xSocket, SOCKETS_SHUT_RDWR ); } else { //failed to connect to server } SOCKETS_Close( xSocket ); }
For a full example, see the Secure Sockets echo client demo.
Porting
FreeRTOS Secure Sockets depends on a TCP/IP stack and on a TLS implementation. Depending on your stack, to port the Secure Sockets library, you might need to port some of the following:
-
The FreeRTOS+TCP
TCP/IP stack
For more information about porting, see Porting the Secure Sockets Library in the FreeRTOS Porting Guide.