Self-managed certificate signing using Amazon IoT Core certificate provider
You can create an Amazon IoT Core certificate provider to sign certificate signing requests
(CSRs) in Amazon IoT fleet provisioning. A certificate provider references a Lambda function
and the CreateCertificateFromCsr MQTT API for fleet provisioning
When you don't have a certificate provider with your Amazon Web Services account, the CreateCertificateFromCsr MQTT API is called in fleet provisioning to generate the certificate from a CSR. After you create a certificate provider, the behavior of the CreateCertificateFromCsr MQTT API will change and all calls to this MQTT API will invoke the certificate provider to issue the certificate.
With Amazon IoT Core certificate provider, you can implement solutions that utilize private
certificate authorities (CAs) such as Amazon Private CA
Important
You can only create one certificate provider per Amazon Web Services account. The signing behavior change applies to the entire fleet that calls the CreateCertificateFromCsr MQTT API until you delete the certificate provider from your Amazon Web Services account.
In this topic:
How self-managed certificate signing works in fleet provisioning
Key concepts
The following concepts provide details that can help you understand how self-managed certificate signing works in Amazon IoT fleet provisioning. For more information, see Provisioning devices that don't have device certificates using fleet provisioning.
- Amazon IoT fleet provisioning
-
With Amazon IoT fleet provisioning (short for fleet provisioning), Amazon IoT Core generates and securely delivers device certificates to your devices when they connect to Amazon IoT Core for the first time. You can use fleet provisioning to connect devices that don't have device certificates to Amazon IoT Core.
- Certificate signing request (CSR)
-
In the process of fleet provisioning, a device makes a request to Amazon IoT Core through the fleet provisioning MQTT APIs. This request includes a certificate signing request (CSR), which will be signed to create a client certificate.
- Amazon managed certificate signing in fleet provisioning
-
Amazon managed is the default setting for certificate signing in fleet provisioning. With Amazon managed certificate signing, Amazon IoT Core will sign CSRs using its own CAs.
- Self-managed certificate signing in fleet provisioning
-
Self-managed is another option for certificate signing in fleet provisioning. With self-managed certificate signing, you create an Amazon IoT Core certificate provider to sign CSRs. You can use self-managed certificate signing to sign CSRs with a CA generated by Amazon Private CA, other publicly trusted CA, or your own Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
- Amazon IoT Core certificate provider
-
Amazon IoT Core certificate provider (short for certificate provider) is a customer-managed resource that's used for self-managed certificate signing in fleet provisioning.
Diagram
The following diagram is a simplified illustration of how self-certificate signing works in Amazon IoT fleet provisioning.
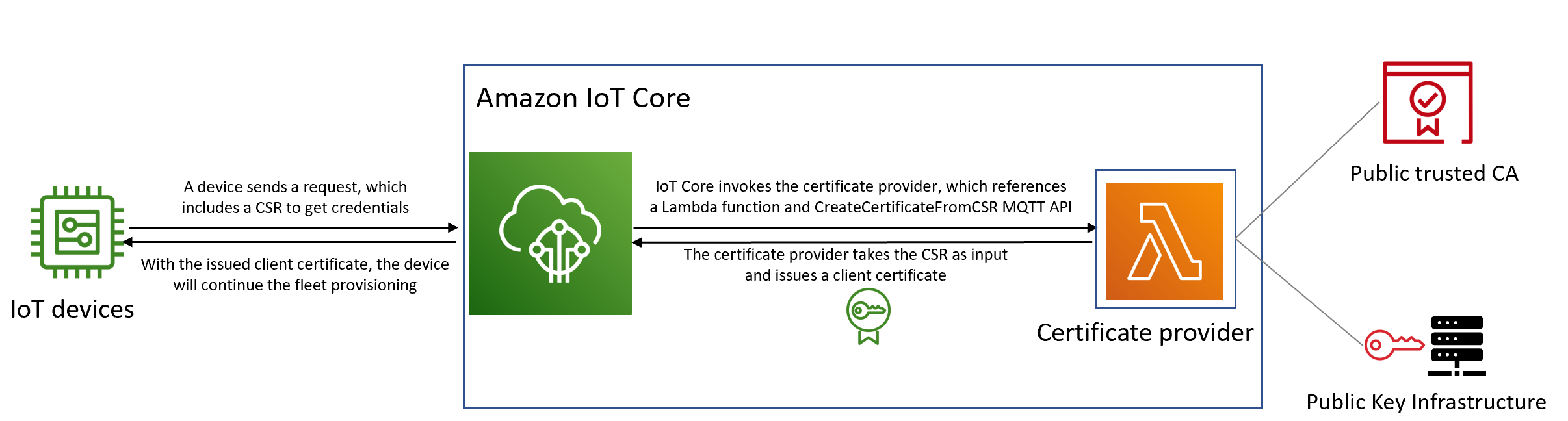
-
When a new IoT device is manufactured or introduced to the fleet, it needs client certificates to authenticate itself with Amazon IoT Core.
-
As part of the fleet provisioning process, the device makes a request to Amazon IoT Core for client certificates through the fleet provisioning MQTT APIs. This request includes a certificate signing request (CSR).
-
Amazon IoT Core invokes the certificate provider and passes the CSR as input to the provider.
-
The certificate provider takes the CSR as input and issues a client certificate.
For Amazon managed certificate signing, Amazon IoT Core signs the CSR using its own CA and issues a client certificate.
-
With the issued client certificate, the device will continue the fleet provisioning and establish a secure connection with Amazon IoT Core.
Certificate provider Lambda function input
Amazon IoT Core sends the following object to the Lambda function when a device registers
with it. The value of certificateSigningRequest is the CSR in Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) formatCreateCertificateFromCsr request. The principalId is
the ID of the principal used to connect to Amazon IoT Core when making the
CreateCertificateFromCsr request. clientId is the
client ID set for the MQTT connection.
{ "certificateSigningRequest": "string", "principalId": "string", "clientId": "string" }
Certificate provider Lambda function return value
The Lambda function must return a response that contains the
certificatePem value. The following is an example of a successful
response. Amazon IoT Core will use the return value (certificatePem) to
create the certificate.
{ "certificatePem": "string" }
If the registration is successful, CreateCertificateFromCsr will
return the same certificatePem in the
CreateCertificateFromCsr response. For more information, see the
response payload example of CreateCertificateFromCsr
Example Lambda function
Before creating a certificate provider, you must create a Lambda function to sign a
CSR. The following is an example Lambda function in Python. This function calls Amazon Private CA
to sign the input CSR, using a private CA and the SHA256WITHRSA signing
algorithm. The returned client certificate will be valid for one year. For more
information about Amazon Private CA and how to create a private CA, see What is Amazon Private CA?
Note
Amazon Private Certificate Authority isn't available in China Regions. If you want to use self-managed certificate signing in China, replace the private CA with a CA generated by other public trusted CAs or your own Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) in the following code example.
import os import time import uuid import boto3 def lambda_handler(event, context): ca_arn = os.environ['CA_ARN'] csr = (event['certificateSigningRequest']).encode('utf-8') acmpca = boto3.client('acm-pca') cert_arn = acmpca.issue_certificate( CertificateAuthorityArn=ca_arn, Csr=csr, Validity={"Type": "DAYS", "Value": 365}, SigningAlgorithm='SHA256WITHRSA', IdempotencyToken=str(uuid.uuid4()) )['CertificateArn'] # Wait for certificate to be issued time.sleep(1) cert_pem = acmpca.get_certificate( CertificateAuthorityArn=ca_arn, CertificateArn=cert_arn )['Certificate'] return { 'certificatePem': cert_pem }
Important
-
Certificates returned by the Lambda function must have the same subject name and public key as the Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
-
The Lambda function must finish running in 5 seconds.
-
The Lambda function must be in the same Amazon Web Services account and Region as the certificate provider resource.
-
The Amazon IoT service principal must be granted the invoke permission to the Lambda function. To avoid confused deputy issues, we recommend that you set
sourceArnandsourceAccountfor the invoke permissions. For more information, see Cross-service confused deputy prevention.
The following resource-based policy example for Lambda grants Amazon IoT the permission to invoke the Lambda function:
-
{ "Version":"2012-10-17", "Id": "InvokePermission", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "LambdaAllowIotProvider", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "iot.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction", "Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-function", "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "AWS:SourceAccount": "123456789012" }, "ArnLike": { "AWS:SourceArn": "arn:aws:iot:us-east-1:123456789012:certificateprovider/my-certificate-provider" } } } ] }
Self-managed certificate signing for fleet provisioning
You can choose self-managed certificate signing for fleet provisioning using Amazon CLI or Amazon Web Services Management Console.
To choose self-managed certificate signing, you must create an Amazon IoT Core
certificate provider to sign CSRs in fleet provisioning. Amazon IoT Core invokes
the certificate provider, which takes a CSR as input and returns a client
certificate. To create a certificate provider, use the
CreateCertificateProvider API operation or the
create-certificate-provider CLI command.
Note
After you create a certificate provider, the behavior of CreateCertificateFromCsr API for fleet
provisioningCreateCertificateFromCsr will invoke the certificate
provider to create the certificates. It can take a few minutes for this
behavior to change after a certificate provider is created.
aws iot create-certificate-provider \ --certificateProviderNamemy-certificate-provider\ --lambdaFunctionArnarn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-function-1\ --accountDefaultForOperations CreateCertificateFromCsr
The following shows an example output for this command:
{ "certificateProviderName": "my-certificate-provider", "certificateProviderArn": "arn:aws:iot:us-east-1:123456789012:certificateprovider:my-certificate-provider" }
For more information, see CreateCertificateProvider from the Amazon IoT
API Reference.
To choose self-managed certificate signing using Amazon Web Services Management Console, follow the steps:
-
Go to the Amazon IoT console
. -
On the left navigation, under Security, choose Certificate signing.
-
On the Certificate signing page, under Certificate signing details, choose Edit certificate signing method.
-
On the Edit certificate signing method page, under Certificate signing method, choose Self-managed.
-
In the Self-managed settings section, enter a name for certificate provider, then create or choose a Lambda function.
-
Choose Update certificate signing.
Amazon CLI commands for certificate provider
Create certificate provider
To create a certificate provider, use the
CreateCertificateProvider API operation or the
create-certificate-provider CLI command.
Note
After you create a certificate provider, the behavior of CreateCertificateFromCsr API for fleet
provisioningCreateCertificateFromCsr will invoke the certificate
provider to create the certificates. It can take a few minutes for this
behavior to change after a certificate provider is created.
aws iot create-certificate-provider \ --certificateProviderNamemy-certificate-provider\ --lambdaFunctionArnarn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-function-1\ --accountDefaultForOperations CreateCertificateFromCsr
The following shows an example output for this command:
{ "certificateProviderName": "my-certificate-provider", "certificateProviderArn": "arn:aws:iot:us-east-1:123456789012:certificateprovider:my-certificate-provider" }
For more information, see CreateCertificateProvider from the Amazon IoT
API Reference.
Update certificate provider
To update a certificate provider, use the
UpdateCertificateProvider API operation or the
update-certificate-provider CLI command.
aws iot update-certificate-provider \ --certificateProviderNamemy-certificate-provider\ --lambdaFunctionArnarn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-function-2\ --accountDefaultForOperations CreateCertificateFromCsr
The following shows an example output for this command:
{ "certificateProviderName": "my-certificate-provider", "certificateProviderArn": "arn:aws:iot:us-east-1:123456789012:certificateprovider:my-certificate-provider" }
For more information, see UpdateCertificateProvider from the Amazon IoT API
Reference.
Describe certificate provider
To describe a certificate provider, use the
DescribeCertificateProvider API operation or the
describe-certificate-provider CLI command.
aws iot describe-certificate-provider --certificateProviderNamemy-certificate-provider
The following shows an example output for this command:
{ "certificateProviderName": "my-certificate-provider", "lambdaFunctionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-function", "accountDefaultForOperations": [ "CreateCertificateFromCsr" ], "creationDate": "2022-11-03T00:15", "lastModifiedDate": "2022-11-18T00:15" }
For more information, see DescribeCertificateProvider from the Amazon IoT
API Reference.
Delete certificate provider
To delete a certificate provider, use the
DeleteCertificateProvider API operation or the
delete-certificate-provider CLI command. If you delete the
certificate provider resource, the behavior of
CreateCertificateFromCsr will resume, and Amazon IoT will create
certificates signed by Amazon IoT from a CSR.
aws iot delete-certificate-provider --certificateProviderNamemy-certificate-provider
This command doesn't produce any output.
For more information, see DeleteCertificateProvider from the Amazon IoT
API Reference.
List certificate provider
To list the certificate providers within your Amazon Web Services account, use the
ListCertificateProviders API operation or the
list-certificate-providers CLI command.
aws iot list-certificate-providers
The following shows an example output for this command:
{ "certificateProviders": [ { "certificateProviderName": "my-certificate-provider", "certificateProviderArn": "arn:aws:iot:us-east-1:123456789012:certificateprovider:my-certificate-provider" } ] }
For more information, see ListCertificateProvider from the Amazon IoT
API Reference.