Using Map state in Distributed mode for large-scale parallel workloads in Step Functions
Managing state and transforming data
Learn about Passing data between states with variables and Transforming data with JSONata.
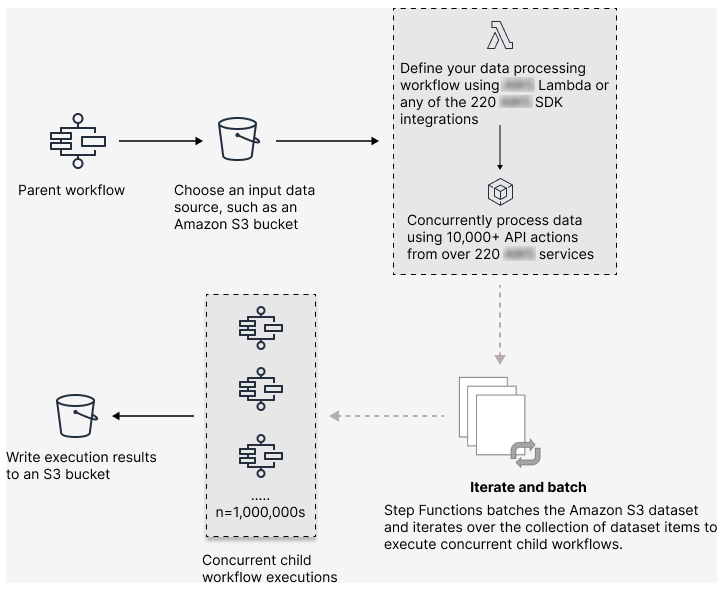
With Step Functions, you can orchestrate large-scale parallel workloads to perform tasks, such as on-demand processing of semi-structured data. These parallel workloads let you concurrently process large-scale data sources stored in Amazon S3. For example, you might process a single JSON or CSV file that contains large amounts of data. Or you might process a large set of Amazon S3 objects.
To set up a large-scale parallel workload in your workflows, include a Map
state in Distributed mode. The Map state processes items
in a dataset concurrently. A Map state set to Distributed is known as a Distributed Map state. In Distributed
mode, the Map state allows
high-concurrency
processing. In Distributed mode, the Map state processes the items in the
dataset in iterations called child workflow executions. You can specify
the number of child workflow executions that can run in
parallel.
Each child workflow execution has its own, separate execution history from that of the
parent workflow. If you don't specify, Step Functions runs 10,000 parallel child workflow executions
in parallel.
The following illustration explains how you can set up large-scale parallel workloads in your workflows.
Learn in a workshop
Learn how serverless technologies such as Step Functions and Lambda can simplify management and scaling, offload undifferentiated tasks, and address the challenges of large-scale distributed data processing. Along the way, you will work with distributed map for high concurrency processing. The workshop also presents best practices for optimizing your workflows, and practical use cases for claims processing, vulnerability scanning, and Monte Carlo simulation.
In this topic
Key terms
- Distributed mode
-
A processing mode of the Map state. In this mode, each iteration of the
Mapstate runs as a child workflow execution that enables high concurrency. Each child workflow execution has its own execution history, which is separate from the parent workflow's execution history. This mode supports reading input from large-scale Amazon S3 data sources. - Distributed Map state
-
A Map state set to Distributed processing mode.
- Map workflow
A set of steps that a
Mapstate runs.- Parent workflow
-
A workflow that contains one or more Distributed Map states.
- Child workflow execution
-
An iteration of the Distributed Map state. A child workflow execution has its own execution history, which is separate from the parent workflow's execution history.
- Map Run
-
When you run a
Mapstate in Distributed mode, Step Functions creates a Map Run resource. A Map Run refers to a set of child workflow executions that a Distributed Map state starts, and the runtime settings that control these executions. Step Functions assigns an Amazon Resource Name (ARN) to your Map Run. You can examine a Map Run in the Step Functions console. You can also invoke theDescribeMapRunAPI action.Child workflow executions of a Map Run emit metrics to CloudWatch;. These metrics will have a labelled State Machine ARN with the following format:
arn:partition:states:region:account:stateMachine:stateMachineName/MapRunLabel or UUIDFor more information, see Viewing Map Runs.
Distributed Map state definition example (JSONPath)
Use the Map state in Distributed mode when you need to orchestrate large-scale parallel workloads that meet any combination of the following conditions:
The size of your dataset exceeds 256 KiB.
The workflow's execution event history would exceed 25,000 entries.
You need a concurrency of more than 40 concurrent iterations.
The following Distributed Map state definition example specifies the dataset as a CSV file stored in an Amazon S3 bucket. It also specifies a Lambda function that processes the data in each row of the CSV file. Because this example uses a CSV file, it also specifies the location of the CSV column headers. To view the complete state machine definition of this example, see the tutorial Copying large-scale CSV data using Distributed Map.
{
"Map": {
"Type": "Map",
"ItemReader": {
"ReaderConfig": {
"InputType": "CSV",
"CSVHeaderLocation": "FIRST_ROW"
},
"Resource": "arn:aws-cn:states:::s3:getObject",
"Parameters": {
"Bucket": "amzn-s3-demo-bucket",
"Key": "csv-dataset/ratings.csv"
}
},
"ItemProcessor": {
"ProcessorConfig": {
"Mode": "DISTRIBUTED",
"ExecutionType": "EXPRESS"
},
"StartAt": "LambdaTask",
"States": {
"LambdaTask": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws-cn:states:::lambda:invoke",
"OutputPath": "$.Payload",
"Parameters": {
"Payload.$": "$",
"FunctionName": "arn:aws-cn:lambda:us-west-2:account-id:function:processCSVData"
},
"End": true
}
}
},
"Label": "Map",
"End": true,
"ResultWriter": {
"Resource": "arn:aws-cn:states:::s3:putObject",
"Parameters": {
"Bucket": "amzn-s3-demo-destination-bucket",
"Prefix": "csvProcessJobs"
}
}
}
}Permissions to run Distributed Map
When you include a Distributed Map state in your workflows, Step Functions needs appropriate permissions to allow the state machine role to invoke the StartExecution API action for the Distributed Map state.
The following IAM policy example grants the least privileges required to your state machine role for running the Distributed Map state.
Note
Make sure that you replace stateMachineNamearn:aws-cn:states:.region:account-id:stateMachine:mystateMachine
-
{ "Version":"2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "states:StartExecution" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws-cn:states:us-east-1:123456789012:stateMachine:myStateMachineName" ] }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "states:DescribeExecution" ], "Resource": "arn:aws-cn:states:us-east-1:123456789012:execution:myStateMachineName:*" } ] }
In addition, you need to make sure that you have the least privileges necessary to access the Amazon resources used in the Distributed Map state, such as Amazon S3 buckets. For information, see IAM policies for using Distributed Map states.
Distributed Map state fields
To use the Distributed Map state in your workflows, specify one or more of these fields. You specify these fields in addition to the common state fields.
Type(Required)-
Sets the type of state, such as
Map. ItemProcessor(Required)-
Contains the following JSON objects that specify the
Mapstate processing mode and definition.-
ProcessorConfig– JSON object that specifies the mode for processing items, with the following sub-fields:-
Mode– Set toDISTRIBUTEDto use theMapstate in Distributed mode.Warning
Distributed mode is supported in Standard workflows but not supported in Express workflows.
-
ExecutionType– Specifies the execution type for the Map workflow as either STANDARD or EXPRESS. You must provide this field if you specifiedDISTRIBUTEDfor theModesub-field. For more information about workflow types, see Choosing workflow type in Step Functions.
-
StartAt– Specifies a string that indicates the first state in a workflow. This string is case-sensitive and must match the name of one of the state objects. This state runs first for each item in the dataset. Any execution input that you provide to theMapstate passes to theStartAtstate first.States– A JSON object containing a comma-delimited set of states. In this object, you define the Map workflow.
-
ItemReader-
Specifies a dataset and its location. The
Mapstate receives its input data from the specified dataset.In Distributed mode, you can use either a JSON payload passed from a previous state or a large-scale Amazon S3 data source as the dataset. For more information, see ItemReader (Map).
Items(Optional, JSONata only)-
A JSON array, a JSON object, or a JSONata expression that must evaluate to an array or object.
ItemsPath(Optional, JSONPath only)-
Specifies a reference path using the JsonPath
syntax to select the JSON node that contains an array of items or an object with key-value pairs inside the state input. In Distributed mode, you specify this field only when you use a JSON array or object from a previous step as your state input. For more information, see ItemsPath (Map, JSONPath only).
ItemSelector(Optional, JSONPath only)-
Overrides the values of individual dataset items before they're passed on to each
Mapstate iteration.In this field, you specify a valid JSON input that contains a collection of key-value pairs. These pairs can either be static values that you define in your state machine definition, values selected from the state input using a path, or values accessed from the context object. For more information, see ItemSelector (Map).
ItemBatcher(Optional)-
Specifies to process the dataset items in batches. Each child workflow execution then receives a batch of these items as input. For more information, see ItemBatcher (Map).
MaxConcurrency(Optional)-
Specifies the number of child workflow executions that can run in parallel. The interpreter only allows up to the specified number of parallel child workflow executions. If you don't specify a concurrency value or set it to zero, Step Functions doesn't limit concurrency and runs 10,000 parallel child workflow executions. In JSONata states, you can specify a JSONata expression that evaluates to an integer.
Note
While you can specify a higher concurrency limit for parallel child workflow executions, we recommend that you don't exceed the capacity of a downstream Amazon service, such as Amazon Lambda.
MaxConcurrencyPath(Optional, JSONPath only)-
If you want to provide a maximum concurrency value dynamically from the state input using a reference path, use
MaxConcurrencyPath. When resolved, the reference path must select a field whose value is a non-negative integer.Note
A
Mapstate cannot include bothMaxConcurrencyandMaxConcurrencyPath. ToleratedFailurePercentage(Optional)-
Defines the percentage of failed items to tolerate in a Map Run. The Map Run automatically fails if it exceeds this percentage. Step Functions calculates the percentage of failed items as the result of the total number of failed or timed out items divided by the total number of items. You must specify a value between zero and 100. For more information, see Setting failure thresholds for Distributed Map states in Step Functions.
In JSONata states, you can specify a JSONata expression that evaluates to an integer.
ToleratedFailurePercentagePath(Optional, JSONPath only)-
If you want to provide a tolerated failure percentage value dynamically from the state input using a reference path, use
ToleratedFailurePercentagePath. When resolved, the reference path must select a field whose value is between zero and 100. ToleratedFailureCount(Optional)-
Defines the number of failed items to tolerate in a Map Run. The Map Run automatically fails if it exceeds this number. For more information, see Setting failure thresholds for Distributed Map states in Step Functions.
In JSONata states, you can specify a JSONata expression that evaluates to an integer.
ToleratedFailureCountPath(Optional, JSONPath only)-
If you want to provide a tolerated failure count value dynamically from the state input using a reference path, use
ToleratedFailureCountPath. When resolved, the reference path must select a field whose value is a non-negative integer. Label(Optional)-
A string that uniquely identifies a
Mapstate. For each Map Run, Step Functions adds the label to the Map Run ARN. The following is an example of a Map Run ARN with a custom label nameddemoLabel:arn:aws-cn:states:region:account-id:mapRun:demoWorkflow/demoLabel:3c39a231-69bb-3d89-8607-9e124eddbb0bIf you don't specify a label, Step Functions automatically generates a unique label.
Note
Labels can't exceed 40 characters in length, must be unique within a state machine definition, and can't contain any of the following characters:
-
Whitespace
-
Wildcard characters (
? *) -
Bracket characters (
< > { } [ ]) -
Special characters (
: ; , \ | ^ ~ $ # % & ` ") -
Control characters (
\\u0000-\\u001for\\u007f-\\u009f).
Step Functions accepts names for state machines, executions, activities, and labels that contain non-ASCII characters. Because such characters will prevent Amazon CloudWatch from logging data, we recommend using only ASCII characters so you can track Step Functions metrics.
-
ResultWriter(Optional)-
Specifies the Amazon S3 location where Step Functions writes all child workflow execution results.
Step Functions consolidates all child workflow execution data, such as execution input and output, ARN, and execution status. It then exports executions with the same status to their respective files in the specified Amazon S3 location. For more information, see ResultWriter (Map).
If you don't export the
Mapstate results, it returns an array of all the child workflow execution results. For example:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] ResultPath(Optional, JSONPath only)-
Specifies where in the input to place the output of the iterations. The input is then filtered as specified by the OutputPath field if present, before it is passed as the state's output. For more information, see Input and Output Processing.
ResultSelector(Optional)-
Pass a collection of key-value pairs, where the values are static or selected from the result. For more information, see ResultSelector.
Tip
If the Parallel or Map state you use in your state machines returns an array of arrays, you can transform them into a flat array with the ResultSelector field. For more information, see Flattening an array of arrays.
Retry(Optional)-
An array of objects, called Retriers, that define a retry policy. An execution uses the retry policy if the state encounters runtime errors. For more information, see State machine examples using Retry and Catch.
Note
If you define Retriers for the Distributed Map state, the retry policy applies to all of the child workflow executions the
Mapstate started. For example, imagine yourMapstate started three child workflow executions, out of which one fails. When the failure occurs, the execution uses theRetryfield, if defined, for theMapstate. The retry policy applies to all the child workflow executions and not just the failed execution. If one or more child workflow executions fails, the Map Run fails.When you retry a
Mapstate, it creates a new Map Run. Catch(Optional)-
An array of objects, called Catchers, that define a fallback state. Step Functions uses the Catchers defined in
Catchif the state encounters runtime errors. When an error occurs, the execution first uses any retriers defined inRetry. If the retry policy isn't defined or is exhausted, the execution uses its Catchers, if defined. For more information, see Fallback States. Output(Optional, JSONata only)-
Used to specify and transform output from the state. When specified, the value overrides the state output default.
The output field accepts any JSON value (object, array, string, number, boolean, null). Any string value, including those inside objects or arrays, will be evaluated as JSONata if surrounded by {% %} characters.
Output also accepts a JSONata expression directly, for example: "Output": "{% jsonata expression %}"
For more information, see Transforming data with JSONata in Step Functions.
-
Assign(Optional) -
Used to store variables. The
Assignfield accepts a JSON object with key/value pairs that define variable names and their assigned values. Any string value, including those inside objects or arrays, will be evaluated as JSONata when surrounded by{% %}charactersFor more information, see Passing data between states with variables.
Setting failure thresholds for Distributed Map states in Step Functions
When you orchestrate large-scale parallel workloads, you can also define a tolerated failure threshold. This value lets you specify the maximum number of, or percentage of, failed items as a failure threshold for a Map Run. Depending on which value you specify, your Map Run fails automatically if it exceeds the threshold. If you specify both values, the workflow fails when it exceeds either value.
Specifying a threshold helps you fail a specific number of items before the entire
Map Run fails. Step Functions returns a States.ExceedToleratedFailureThreshold error when the Map Run fails because the
specified threshold is exceeded.
Note
Step Functions may continue to run child workflows in a Map Run even after the tolerated failure threshold is exceeded, but before the Map Run fails.
To specify the threshold value in Workflow Studio, select Set a tolerated failure threshold in Additional configuration under the Runtime settings field.
- Tolerated failure percentage
-
Defines the percentage of failed items to tolerate. Your Map Run fails if this value is exceeded. Step Functions calculates the percentage of failed items as the result of the total number of failed or timed out items divided by the total number of items. You must specify a value between zero and 100. The default percentage value is zero, which means that the workflow fails if any one of its child workflow executions fails or times out. If you specify the percentage as 100, the workflow won’t fail even if all child workflow executions fail.
Alternatively, you can specify the percentage as a reference path to an existing key-value pair in your Distributed Map state input. This path must resolve to a positive integer between 0 and 100 at runtime. You specify the reference path in the
ToleratedFailurePercentagePathsub-field.For example, given the following input:
{"percentage":15}You can specify the percentage using a reference path to that input as follows:
{ ... "Map": { "Type": "Map", ..."ToleratedFailurePercentagePath":"$.percentage"... } }Important
You can specify either
ToleratedFailurePercentageorToleratedFailurePercentagePath, but not both in your Distributed Map state definition. - Tolerated failure count
-
Defines the number of failed items to tolerate. Your Map Run fails if this value is exceeded.
Alternatively, you can specify the count as a reference path to an existing key-value pair in your Distributed Map state input. This path must resolve to a positive integer at runtime. You specify the reference path in the
ToleratedFailureCountPathsub-field.For example, given the following input:
{"count":10}You can specify the number using a reference path to that input as follows:
{ ... "Map": { "Type": "Map", ..."ToleratedFailureCountPath":"$.count"... } }Important
You can specify either
ToleratedFailureCountorToleratedFailureCountPath, but not both in your Distributed Map state definition.
Learn more about distributed maps
To continue learning more about Distributed Map state, see the following resources:
-
Input and output processing
To configure the input that a Distributed Map state receives and the output that it generates, Step Functions provides the following fields:
In addition to these fields, Step Functions also provides you the ability to define a tolerated failure threshold for Distributed Map. This value lets you specify the maximum number of, or percentage of, failed items as a failure threshold for a Map Run. For more information about configuring the tolerated failure threshold, see Setting failure thresholds for Distributed Map states in Step Functions.
-
Using Distributed Map state
Refer the following tutorials and sample projects to get started with using Distributed Map state.
-
Examine Distributed Map state execution
The Step Functions console provides a Map Run Details page, which displays all the information related to a Distributed Map state execution. For information about how to examine the information displayed on this page, see Viewing Map Runs.