Using SAML identity providers with a user pool
You can choose to have your web and mobile app users sign in through a SAML identity
provider (IdP) like Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
With managed login, Amazon Cognito authenticates local and third-party IdP users and issues JSON web tokens (JWTs). With the tokens that Amazon Cognito issues, you can consolidate multiple identity sources into a universal OpenID Connect (OIDC) standard across all of your apps. Amazon Cognito can process SAML assertions from your third-party providers into that SSO standard. You can create and manage a SAML IdP in the Amazon Web Services Management Console, through the Amazon CLI, or with the Amazon Cognito user pools API. To create your first SAML IdP in the Amazon Web Services Management Console, see Adding and managing SAML identity providers in a user pool.
Note
Federation with sign-in through a third-party IdP is a feature of Amazon Cognito user pools. Amazon Cognito identity pools, sometimes called Amazon Cognito federated identities, are an implementation of federation that you must set up separately in each identity pool. A user pool can be a third-party IdP to an identity pool. For more information, see Amazon Cognito identity pools.
Quick reference for IdP configuration
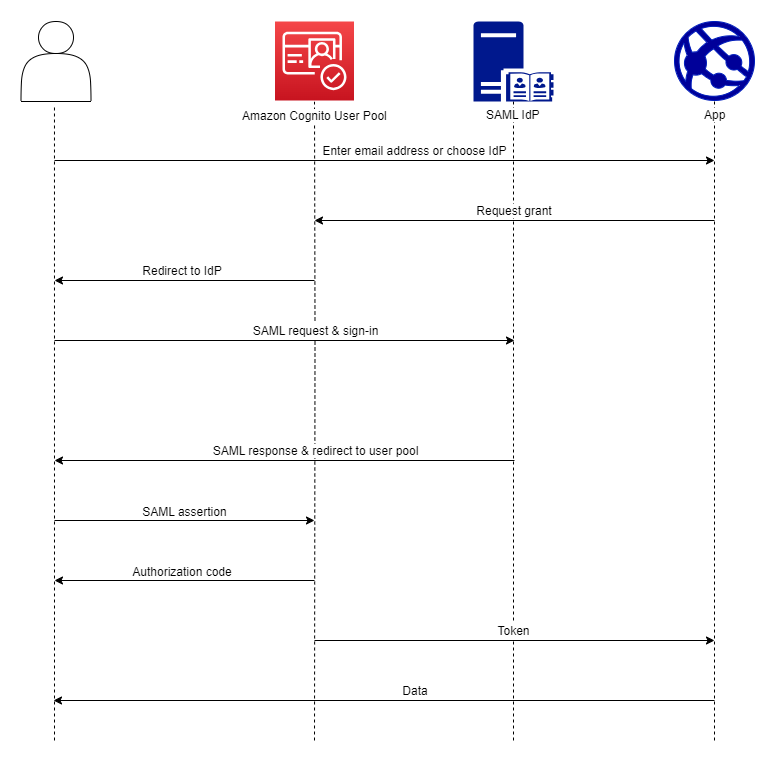
You must configure your SAML IdP to accept request and send responses to your user pool. The documentation for your SAML IdP will contain information about how to add your user pool as a relying party or application for your SAML 2.0 IdP. The documentation that follows provides the values that you must provide for the SP entity ID and assertion consumer service (ACS) URL.
User pool SAML values quick reference
- SP entity ID
-
urn:amazon:cognito:sp:us-east-1_EXAMPLE - ACS URL
-
https://Your user pool domain/saml2/idpresponse
You must configure your user pool to support your identity provider. The high-level steps to add an external SAML IdP are as follows.
-
Download SAML metadata from your IdP, or retrieve the URL to your metadata endpoint. See Configuring your third-party SAML identity provider.
-
Add a new IdP to your user pool. Upload the SAML metadata or provide the metadata URL. See Adding and managing SAML identity providers in a user pool.
-
Assign the IdP to your app clients. See Application-specific settings with app clients.
Topics
Case sensitivity of SAML user names
When a federated user attempts to sign in, the SAML identity provider (IdP) passes
a unique NameId to Amazon Cognito in the user's SAML assertion. Amazon Cognito identifies
a SAML-federated user by their NameId claim. Regardless of the case
sensitivity settings of your user pool, Amazon Cognito recognizes a returning federated user
from a SAML IdP when they pass their unique and case-sensitive NameId
claim. If you map an attribute like email to NameId, and
your user changes their email address, they can't sign in to your app.
Map NameId in your SAML assertions from an IdP attribute that has
values that don't change.
For example, Carlos has a user profile in your case-insensitive user pool from an
Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) SAML assertion that passed a
NameId value of Carlos@example.com. The next time
Carlos attempts to sign in, your ADFS IdP passes a NameId value of
carlos@example.com. Because NameId must be an exact
case match, the sign-in doesn't succeed.
If your users can't log in after their NameID changes, delete their
user profiles from your user pool. Amazon Cognito will create new user profiles the next time
they sign in.